Analyzing Safety Practices in Construction
The construction industry is essential but dangerous, with workers exposed to multiple risks like falls, machine hazards, and chemical exposures. Safety interventions, like pre-task planning (PTP) and personal protective equipment (PPE), mitigate these dangers. The latest Data Bulletin of the Center For Construction Research and Training (CPWR) analyzes the safety practices of contractors and their relationship with unions and trade associations.
The survey categorized respondents by union and trade association status. Most respondents hired union workers, with 36.2% solely employing them and 24.8% employing both union and non-union workers. Also, 84.2% were trade association members, and 94.4% of union contractors belonged to trade associations. These factors shape safety practices in the industry.
Pre-Task Planning (PTP)
PTP, essential for identifying and controlling hazards, was analyzed. Contractors employing both union and non-union workers (39.2%) and only union workers (38.9%) reported always conducting PTP, while non-union contractors (19.8%) often did it. Trade association members (35.9%) consistently outperformed non-members (8.5%) in always conducting PTP. PTP involvement varied, with union contractors leading in frontline worker participation.
Top Safety Practices
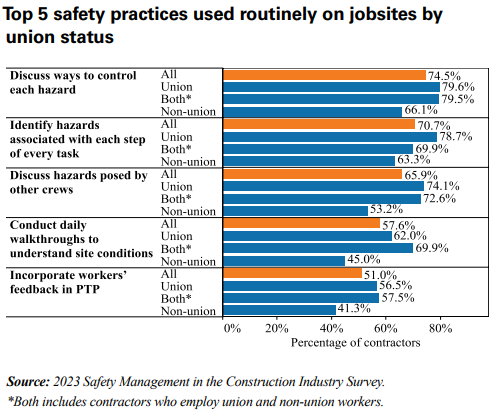 Top safety practices included discussing hazard control (74.5%). Union contractors surpassed non-union ones in implementing these practices, signifying a greater safety commitment.
Top safety practices included discussing hazard control (74.5%). Union contractors surpassed non-union ones in implementing these practices, signifying a greater safety commitment.
PPE Provision
PPE tailored for diverse sizes was crucial. Union contractors (93.5%) excelled in providing individualized PPE, compared to non-union (75.9%) and both-employment (85.1%) contractors. Trade association members (88.8%) outperformed non-members (61.7%). This underscores the need for tailored PPE and trade associations’ advocacy.
Heat-Related Injuries and Strategies
Heat-related injuries concerned the industry. About 62% of union contractors made changes to prevent them, while only 35.3% of non-union contractors did. Contractors with both union and non-union workers had more heat-related injuries (28.4%) than non-union (18.1%) and union contractors (13.9%). Providing water, rest, and shade was the primary strategy, with union contractors leading (96.3%). Union contractors also emphasized worker training (76.9%) and environmental monitoring (58.3%) to manage heat exposure.
The Role of Unions and Trade Associations
Unions and trade associations played pivotal roles in promoting safety. Union contractors consistently demonstrated better safety practices, PPE provision, and safety planning. Trade association membership correlated with improved safety, underlining the importance of industry cooperation in safeguarding construction workers.
The construction industry’s hazardous nature necessitates stringent safety measures. Insights from the 2023 Safety Management in the Construction Industry Survey highlight the substantial impact of unions and trade associations on enhancing safety. As construction accident lawyers, advocating for safety and holding those negligent accountable remains our duty in this challenging but vital industry.
 New York Personal Injury Attorneys Blog
New York Personal Injury Attorneys Blog


